In the realm of cryptocurrency and decentralized finance (DeFi), seeking stable and trustworthy monetary solutions has always been a core challenge. Ethena, as a synthetic dollar protocol built on Ethereum, has introduced its innovative product—USDe—aiming to provide a crypto-native solution for money that does not rely on traditional banking system infrastructure. Ethena's core product, USDe, promises to be fully backed and composable across both centralized finance (CeFi) and DeFi by leveraging assets like Ethereum and Bitcoin through delta hedging.
USDe's stability is primarily achieved through a hedging strategy, which involves holding cryptocurrencies while simultaneously taking opposite positions in the derivatives market to counteract price volatility, thereby maintaining its peg to the U.S. dollar. This strategy encompasses not only the reference value of spot assets but also involves position management in futures markets, allowing USDe to maintain a relatively stable value amidst market fluctuations. Alongside USDe, Ethena has launched the "Internet Bond," a globally accessible, dollar-denominated rewards instrument. The Internet Bond combines revenue from staked assets (like staked Ethereum) with the funding and basis spread from perpetual and futures markets, creating the first on-chain crypto-native monetary solution. This mechanism not only provides a new source of income for holders but also offers an innovative financial tool for the entire crypto ecosystem.
Therefore, this article will delve into the operational principles of Ethena and its stablecoin USDe, its current market impact, and the potential risks and challenges it might face in the future. The aim is to provide investors, developers, and researchers with a comprehensive perspective on the potential and limitations of this emerging financial tool.

Problems Ethena is Trying to Solve
Ethena aims to address one of the largest and most obvious needs in the cryptocurrency market: a decentralized stable asset for crypto. Currently, there is no globally accessible, censorship-resistant way to hold capital in the crypto market. DeFi attempts to create a parallel financial system, but stablecoins, which are the most critical financial instruments, still rely entirely on traditional banking infrastructure. Ethena seeks to provide a scalable, crypto-native form of money to enable a truly independent financial system. For any functional, truly independent financial system to operate at scale, a relatively stable asset not reliant on traditional banking infrastructure is necessary, serving both as a medium of transaction and the core base asset for funding. Without an independent and relatively stable reserve asset, both centralized and decentralized order books are inherently fragile.
Stablecoins are the most important tool in cryptocurrency. All major trading pairs across spot and futures markets in both centralized and decentralized venues are denominated in stablecoins, with over 90% of order book trades and over 70% of on-chain settlements being in stablecoins. In 2023, stablecoins settled more than $12 trillion on-chain, making up two of the five largest assets in the crypto space, accounting for over 40% of the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi, and by far the most utilized assets across decentralized money markets. Centralized exchanges (CEXs) desperately need a reliable and transparent asset to support their order books, while DeFi faces ongoing risks of reliance on USDC or RWA (Real World Assets) with centralized shut-off mechanisms. Reducing dependence on traditional banking systems in stablecoin infrastructure is arguably the single most important issue facing cryptocurrency today.
Simultaneously, most of the 8 billion people worldwide lack permissionless access or the ability to accrue benefits on dollar-denominated capital preservation means. Despite the enormous demand for existing stablecoins, with a total value exceeding $150 billion, their risk profile is typically "return-free." A substantively equivalent product that provides permissionless value accrual represents the largest market opportunity that crypto can offer to individuals globally—a bigger opportunity than either volatile stores of value, fiat, or RWA-backed stablecoins as they currently exist.
So, how does one solve this dilemma? How can one construct a trust-minimized, scalable, and relatively stable asset that does not rely on the banking system, yet systemically generates economic returns at the protocol level and passes these returns to ecosystem participants? Ethena offers a solution: by using derivatives on deep, liquid centralized platforms like CEXs to back assets (including liquid staked assets with inherent yield), USDe aims to directly address the "stablecoin trilemma" that previous decentralized stablecoin designs have encountered, as well as the custodial risk shortcomings of centralized stablecoins.
Ethena's Solution - USDe and Delta Neutrality

Ethena has introduced the stablecoin asset, USDe, to address various challenges currently faced in the market. USDe is a crypto-native synthetic dollar that utilizes spot assets as backing, is managed on-chain, and operates on centralized liquidity platforms. By implementing delta hedging during the minting process, USDe achieves scalability, stability, and resistance to censorship. This approach ensures a dynamic balance in financial markets, allowing USDe to maintain its relative value stability amidst market fluctuations.
Delta hedging refers to using financial instruments (typically derivatives) to offset the risk of changes in the value of spot assets, enabling USDe to function without relying on traditional banking systems. Specifically, delta hedging locks in the asset price through derivatives, ensuring USDe's value remains stable even with significant market volatility. The use of derivatives is key to USDe's ability to scale with high capital efficiency. The depth and liquidity of the derivatives market allow USDe to quickly adjust its asset portfolio in response to changes in supply and demand without the need to increase the quantity of physical assets. This means USDe can expand at a lower capital cost since each USDe requires only a 1:1 "collateral," rather than the over-collateralization often needed by traditional stablecoins. This design not only enhances capital efficiency but also reduces the risk of asset lockup within the system.

Moreover, maintaining dollar stability through hedging strategies is a significant feature of USDe. When minting USDe, the volatility of the asset's value is immediately hedged to achieve Delta neutrality, ensuring that each USDe's value is pegged to the dollar, reducing the risk of value deviation due to market fluctuations. This stability mechanism not only attracts users looking for a stable store of value but also provides convenience for investors wanting to engage in large transactions in the crypto market without taking on high risks.
What is Delta Neutrality? If an investment portfolio has a delta of 0, it can be considered "delta neutral." This means the portfolio is not affected by changes in the underlying asset's value. For example, if Ethena naturally has a positive delta of 1 ETH due to a user providing 1 ETH as backing, by shorting a perpetual contract with a notional position size equal to that 1 ETH, the delta of Ethena's portfolio becomes 0. In other words, when a portfolio is delta neutral, its dollar value remains constant regardless of market conditions (i.e., regardless of how the spot price of ETH changes). The price of ETH could triple and then drop by 90% in a second, but the portfolio's dollar value would remain unaffected (barring temporary dislocations between spot and derivatives markets). This is because any profit from the increase in ETH price is exactly offset by losses from the equally sized short perpetual position.
Resistance to censorship is another core feature of USDe's design. By separating asset custody from traditional banking systems and using a transparent on-chain custody method, USDe avoids the risks associated with assets being controlled by a single entity or institution. Using blockchain technology, the backing assets for USDe are stored in accounts that can be audited programmatically 24/7, ensuring transparency and trustless characteristics. This greatly reduces the likelihood of assets being frozen, seized, or censored, which is crucial for user privacy and asset security.
Furthermore, the design mechanism of USDe also generates protocol-level income, which can be used to support the yield-bearing "Internet Bond" sUSDe alongside USDe. This means that users holding USDe not only benefit from a stable and reliable store of value but can also earn additional returns through sUSDe. This dual incentive mechanism not only enhances the appeal of USDe but also provides an important native "currency" asset to the crypto market, encouraging more capital to flow into the cryptocurrency ecosystem and fostering broader application scenarios.
Sources of Revenue for the Ethena Protocol
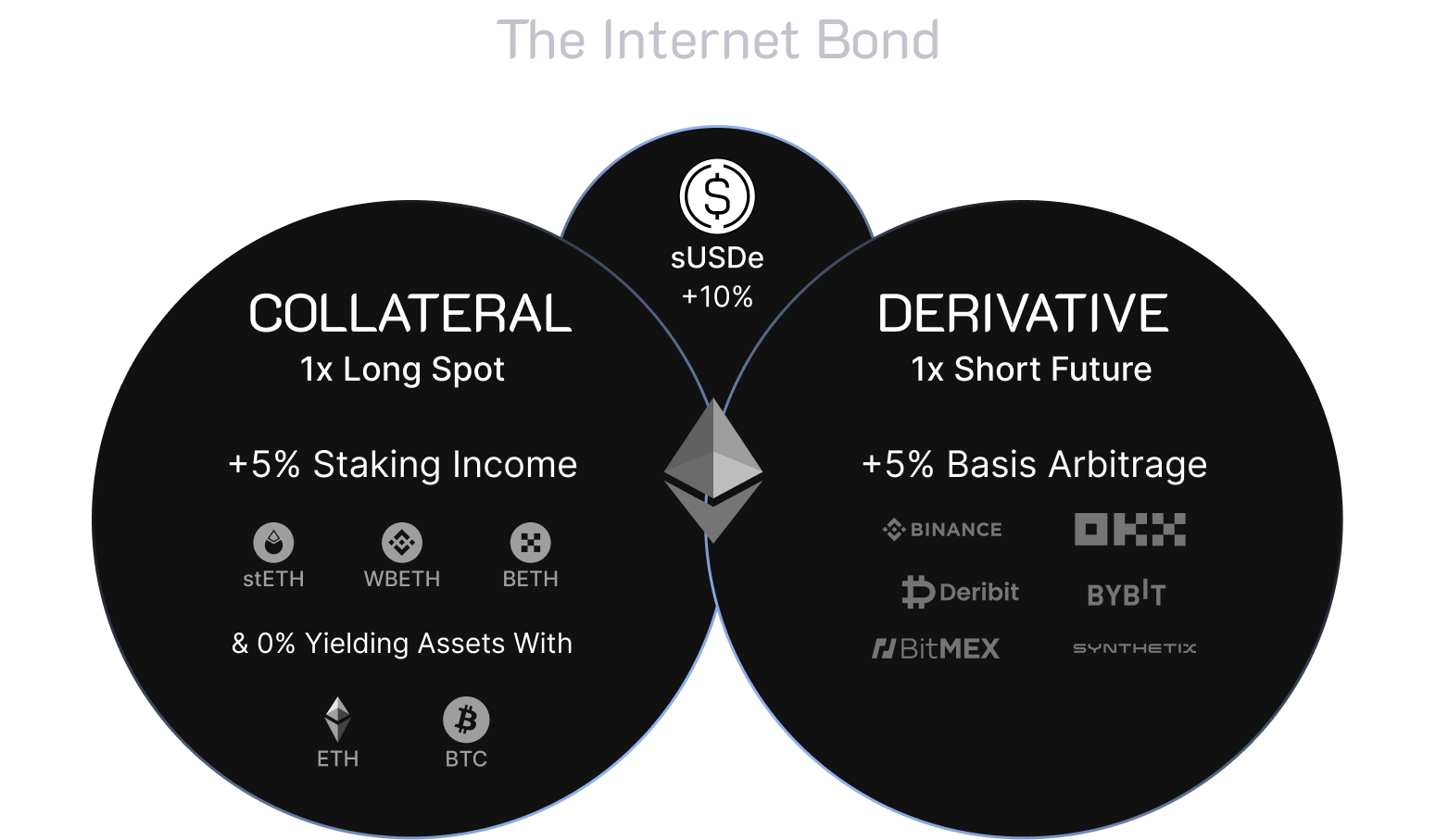
First, by staking Ethereum (ETH), Ethena can earn an annual percentage yield (APY) on the protocol. This process not only increases system liquidity but also provides some returns for the holders of staked ETH.
Second, Ethena uses a Delta hedging strategy in the derivatives market, which includes income from funding fees on derivatives positions and profits from the price differences between futures and spot markets—known as the basis. This hedging strategy allows Ethena to maintain stability amidst market volatility while generating considerable revenue.
Third, Ethena deposits the stablecoin USDC into platforms like Coinbase to earn a fixed annual yield. This provides another stable source of income, which not only enhances Ethena's financial stability but also offers additional value appreciation opportunities for the assets within the system.
Through these diversified income strategies, Ethena not only sustains its operations but also provides various return opportunities for participants within its ecosystem, fostering the development of a stable and profitable cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Users can stake USDe to receive sUSDe and earn staking rewards. The amount of sUSDe a user receives depends on the amount of USDe transferred and the duration of the transfer. Ethena's sUSDe operates under a reward-based "Token Vault" mechanism. The protocol does not re-stake, lend out, or use the deposited USDe for any other purpose. Ethena does not need to take any such actions because the backing mechanism of USDe inherently creates value. When staking USDe, the amount of sUSDe received might be less, but its value is equivalent to USDe. This is a result of the "Token Vault" mechanism, the reward structure, and the ratios defined in the protocol's design.
sUSDe:USDe ratio = (total sUSDe supply) / (total USDe staked + total protocol revenue deposited in USDe terms)@c

Risks Faced by USDe
Ethena's USDe, as a synthetic dollar based on crypto assets, faces several challenges. First, USDe relies on hedging strategies to maintain its peg to the dollar, which means there's a risk of depegging under derivatives market volatility or extreme market conditions. Funding risk is another critical issue; since USDe uses derivatives like perpetual contracts for hedging, during periods of negative funding rates, Ethena will have to pay funding fees, which could affect its overall profitability and stability. However, Ethena has a reserve fund in place that intervenes when the sum of the funding rates for LST assets (like stETH) and short-term perpetual positions is negative, aimed at protecting the spot backing for USDe. Ethena does not pass any "negative income" onto users who stake USDe to get sUSDe.
The risk of exchange bankruptcy is also crucial since Ethena conducts derivatives trading on CEXs. Although mitigated by the "Off-Exchange Settlement" mechanism to reduce direct asset risk, if an exchange goes bankrupt, it could impact profits that are not yet settled. Liquidation risk is controlled through low leverage and tight collateral haircuts, but significant value discrepancies between supporting assets (like stETH) and the hedged contract's underlying asset (like ETH) could still trigger liquidation.
Given that Ethena uses some stETH and other LSTs as margin for delta hedging derivatives positions, the price difference between stETH and ETH is at the core of "collateral risk." Ethena has chosen stETH, whose market share is being eroded by other assets like Mantle's mETH, to minimize this difference. Despite this, since stETH and ETH are not the same asset, Ethena must manage these risks by selecting the most stable LSTs and securing broad industry support. Additionally, while low leverage and strict collateral discounts make the impact of stETH depegging on hedged positions negligible, two major risks remain to be monitored: one, liquidity issues between staking and unstaking ETH and LSTs, potentially causing temporary price differences between stETH and ETH; two, if a critical smart contract error is found in an LST, it could lead to loss of confidence in its integrity, resulting in prolonged exit queues and liquidity depletion. Ethena mitigates these risks by partnering with CeFi and DeFi exchanges, Lido, Binance, and Mantle to increase liquidity and, in extreme scenarios, prepare to convert LSTs into other stable assets to preserve capital.
Custody risk is another risk Ethena faces. Ethena relies on "Off-Exchange Settlement" providers to hold the protocol's backing assets, creating a dependency on their operational capabilities, known as "custody risk." In the crypto space, counterparty risk is always present and now more significant than ever. Custodians' business models are built on securely holding assets rather than leaving collateral with centralized exchanges.
The three primary risks when using off-exchange settlement providers include: (1) Accessibility and availability, where Ethena's ability to deposit, withdraw, and delegate to exchanges might be impaired, and any unavailability or degradation of these functions would hinder trading processes and the minting/redemption functionality of USDe. This should not affect the value of the assets backing USDe; (2) Execution of operational responsibilities, where in the event of an exchange bankruptcy, the protocol relies on cooperation and reasonable legal actions to quickly transfer unrealized profit and loss (PnL) related to the exchange. Ethena mitigates this risk by settling PnL frequently with exchanges, like Copper's Clearloop, which settles PnL daily with exchanges; (3) Operational bankruptcy of the custodian, although the core team has not observed significant operational bankruptcies of major crypto custodians, this risk persists. Even if assets are held in segregated accounts, a custodian's bankruptcy could cause operational issues for USDe creation and redemption because Ethena would need to move assets to another provider.
These backing assets are not owned by the custodian, and neither the custodian nor its creditors have legal claims on these assets due to the use of bankruptcy-remote trusts or MPC wallet solutions by OES providers. Ethena mitigates these risks by avoiding over-concentration of collateral with a single OES provider and managing concentration risk through multiple OES providers within the same exchange. Using Copper's Clearloop as an example, individual custodians provide additional safety measures: never hacked or lost user funds, in stark contrast to DeFi's $7 billion losses; user funds were fully available within days after Coinflex (exchange) went bankrupt; user funds are held in bankruptcy-remote trusts, so even if Copper fails, user funds do not belong to Copper; exchanges provide collateral to Copper in advance to ensure user PnL can be settled each cycle, even if the exchange refuses to settle, Copper can ensure users receive their PnL; Ethena retains the ability to dispute erroneous settlement requests from exchanges.
Conclusion
Ethena's USDe presents a new type of stablecoin based on Ethereum that does not rely on traditional banking systems, achieving dollar peg stability through delta hedging strategies. This innovation challenges existing financial frameworks and provides the crypto ecosystem with a scalable, censorship-resistant form of currency. By combining the holding of spot assets with hedging operations in the futures market, USDe creates a relatively stable store of value and means of transaction. USDe's design cleverly balances the volatility of the crypto market, ensuring the dollar peg under various market conditions. The core of this approach is the delta-neutral strategy, where short positions in derivatives markets offset price changes in spot assets, theoretically keeping USDe's value constant. This stability mechanism not only instills confidence in investors and users but also provides a reliable base currency for DeFi and CeFi platforms.
However, alongside these innovations and opportunities, Ethena and USDe must navigate a series of complex challenges, including but not limited to market volatility risks, legal and regulatory risks, and technical security issues. Ensuring asset security and system resilience against attacks is particularly vital in the crypto domain. Ethena continuously collaborates with industry partners to refine its protocol and risk management strategies to enhance the stability of its stablecoin and user trust.
Overall, Ethena introduces new possibilities to the cryptocurrency market through USDe, aiming to create a stablecoin ecosystem that is independent of traditional financial systems. Realizing this vision requires ongoing innovation, risk management, and close interaction with the community to ensure that, as it progresses, USDe can truly become a reliable "dollar" alternative in the world of cryptocurrencies.

